Nashik, a region celebrated for its agricultural richness, offers diverse climatic conditions that support a wide range of crops. From the cool winters to the hot summers and the heavy monsoons, each season presents unique opportunities for farmers. This blog delves into the best crops suited for Nashik’s climate, season by season, and highlights the importance of soil and petiole testing in optimizing yields. Additionally, we explore how climate adaptation strategies can ensure sustainable farming practices.
Overview of Nashik’s Climate Across Seasons
Nashik experiences distinct climatic variations throughout the year, making it a versatile region for agriculture. The winter season, from November to February, is characterized by cool and dry weather. The summer months, from March to June, are hot and dry, demanding heat-tolerant crops. The monsoon season, from July to October, brings heavy rainfall, necessitating water-resistant crops. Understanding these seasonal variations is crucial for selecting the right crops and implementing effective farming strategies.
Best Crops for Nashik’s Climate in Winter, Summer, and Monsoon
Winter Crops (November – February)
The cool and dry climate of winter in Nashik is ideal for several crops:
- Grapes: Nashik is renowned as the wine capital of India, and winter provides the best conditions for high-quality grape production.
- Onions: One of the most profitable crops in Nashik, onions require well-drained soil to thrive.
- Wheat: This crop grows well in slightly loamy soils with proper moisture retention.
- Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, fenugreek, and coriander flourish in cooler temperatures, making them perfect for winter cultivation.
Summer Crops (March – June)
The hot and dry summers demand heat-tolerant crops:
- Mango: Nashik’s climate supports the growth of high-quality Alphonso and Kesar mangoes.
- Tomatoes: A high-demand crop that benefits from drip irrigation, ensuring consistent water supply.
- Watermelon: Thrives in sandy loam soil with moderate watering, making it a popular summer crop.
- Chili: Requires warm temperatures for better yield, making it an ideal choice for Nashik’s summers.
Monsoon Crops (July – October)
The heavy rains during the monsoon season necessitate the selection of water-resistant crops:
- Paddy: Grown in lowland areas where water stagnation occurs, paddy is a staple monsoon crop.
- Soybeans: A profitable monsoon crop that requires well-drained soil to prevent waterlogging.
- Millets: Jowar and bajra are resilient to fluctuating rainfall, making them suitable for monsoon cultivation.
- Cucumbers: Suitable for Nashik’s fertile soils during the rainy season, cucumbers thrive in moist conditions.
How Soil Type Impacts Grape Cultivation in Nashik
Nashik’s success in grape cultivation is largely due to its favorable climate and soil characteristics. However, not all soil types are equally suitable for growing high-quality grapes. Understanding soil composition and its impact on grape growth is crucial for improving yield, fruit quality, and wine characteristics.
Ideal Soil Conditions for Grape Cultivation
For optimal growth, grapes require:
- Well-drained soil: Excess moisture can lead to root rot and fungal diseases.
- Moderate fertility: Excessive nutrients, especially nitrogen, can lead to excessive vegetative growth, reducing fruit quality.
- Slightly acidic to neutral pH: A pH range of 6.0 to 7.5 is ideal for grapevines.
Types of Soil in Nashik and Their Impact on Grapes
1. Laterite Soil (Red Soil)
Characteristics: Rich in iron and aluminum but poor in organic matter.
Impact on Grapes: Suitable for grape cultivation if properly managed with organic amendments. It helps produce grapes with concentrated flavors, ideal for winemaking.
Management Tip: Adding organic compost and proper irrigation improves soil fertility.
2. Black Cotton Soil
Characteristics: High moisture retention due to clay content, rich in nutrients.
Impact on Grapes: While it retains moisture well, poor drainage can lead to waterlogging, harming grape roots. Suitable for table grapes if drainage is managed.
Management Tip: Raised beds and proper soil aeration techniques can enhance grapevine health.
3. Alluvial Soil
Characteristics: Found near riverbanks, rich in minerals and nutrients.
Impact on Grapes: Excellent for table grapes, as it supports faster growth. However, excess fertility may reduce the concentration of flavors needed for premium wine grapes.
Management Tip: Balanced fertilization is necessary to prevent excessive vegetative growth.
4. Sandy Loam Soil (Most Preferred for Vineyards)
Characteristics: Well-draining, loose structure, rich in minerals.
Impact on Grapes: Ideal for wine grapes as it regulates water supply, enhancing sugar concentration in fruits.
Management Tip: Regular irrigation and organic matter addition maintain soil structure and fertility.
Role of Soil and Petiole Testing in Grape Farming
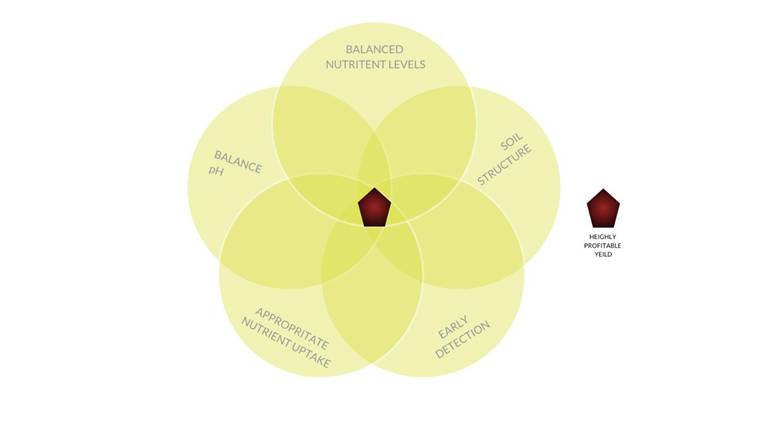
Soil testing before planting helps determine:
- Nutrient levels: Accurate nutrient levels allow for better fertilizer application.
- pH balance: Ensuring the soil has the right pH balance is essential for root absorption and overall vine health.
- Soil structure: Understanding soil structure helps optimize drainage and aeration, preventing issues like waterlogging and root rot.
Petiole testing during the growing season ensures:
- Balanced nutrient uptake: Regular petiole testing helps improve grape yield and quality by ensuring balanced nutrient uptake.
- Early detection of deficiencies: Identifying nutrient deficiencies early can prevent crop loss and ensure healthy grape production
Conclusion
Nashik’s diverse climate and soil types offer unique opportunities for agricultural success. By understanding the best crops for each season and the importance of soil and petiole testing, farmers can optimize yields and ensure sustainable farming practices. ONE LABS stands as a reliable partner in this journey, providing comprehensive testing and customized recommendations to help farmers achieve their yield goals. Whether you are a seasoned farmer or a budding agriculturist, leveraging scientific insights and adapting to climatic variations is key to thriving in Nashik’s dynamic agricultural landscape.
